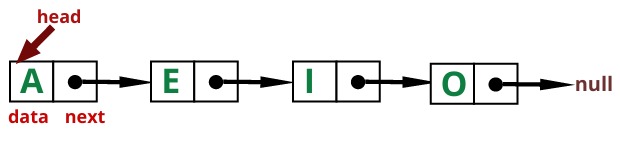
Singly linked list is a collection of nodes that collectively form a linear sequence. In a singly linked list, each node stores data, and as well as a reference to the next node of the list.
Implementation
The linked list instance must keep a reference to the first node of the list, known as the head. If linked
list is empty, then value of head is null.
Our implementation also takes advantage of Java’s support for nested classes, as we define a private
Node class within the scope of the public SinglyLinkedList class. Having
Node as a nested class provides strong encapsulation, shielding users of our class from the
underlying details about nodes and links.
public class SinglyLinkedList<E> {
// instance variables of the SinglyLinkedList
private Node<E> head = null; // head node of the list (or null if empty)
// ---------------- nested Node class ----------------
private static class Node<E> {
private E data;
private Node<E> next;
public Node(E data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// ----------- end of nested Node class -----------
}
Let's create first simple singly linked list with 3 nodes.
public class SinglyLinkedList<E> {
// instance variables of the SinglyLinkedList
private Node<E> head = null; // head node of the list (or null if empty)
// ---------------- nested Node class ----------------
private static class Node<E> {
private E data;
private Node<E> next;
public Node(E data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// ----------- end of nested Node class -----------
/* method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Start with the empty list. */
SinglyLinkedList<Integer> singlyLinkedList = new SinglyLinkedList<Integer>();
// creates 3 nodes
Node<Integer> first = new Node<Integer>(10);
Node<Integer> second = new Node<Integer>(20);
Node<Integer> third = new Node<Integer>(30);
// Three nodes have been allocated dynamically.
// and references to these three blocks as first,
// second and third.
//
// first second third
// | | |
// | | |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
// | 10 | | | 20 | null | | 30 | null |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
// lets assign reference of first to head of singly linked list
singlyLinkedList.head = first;
// Singly linked list head is referencing to first node
//
// singlyLinkedList.head
// and
// first second third
// | | |
// | | |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
// | 10 | | | 20 | null | | 30 | null |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
// assign reference of second node to next of first
first.next = second;
// Now next of first Node refers to second. So they
// both are linked.
//
// singlyLinkedList.head second third
// | | |
// | | |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
// | 10 | -------->| 20 | null | | 30 | null |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+ *
second.next = third; // Link second node with the third node
// Now next of second Node refers to third. So all three
// nodes are linked.
//
// singlyLinkedList.head second third
// | | |
// | | |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
// | 10 | -------->| 20 | -------->| 30 | null |
// +----+------+ +----+------+ +----+------+
}
}
Traversal of singly linked list
In the previous example we have created a singly linked list with three nodes. Now we will write a method to
traverse over a linked list and print the data of the list. Let's give method name as printList.
public class SinglyLinkedList<E> {
// instance variables of the SinglyLinkedList
private Node<E> head = null; // head node of the list (or null if empty)
// ---------------- nested Node class ----------------
private static class Node<E> {
private E data;
private Node<E> next;
public Node(E data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// ----------- end of nested Node class -----------
// instance method of Singly linked list
//which will print the data of nodes starting from the head.
private void printList() {
Node<E> current = this.head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + "--->");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("null");
}
// method to create a simple linked list with 3 nodes
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Start with the empty list.
SinglyLinkedList<Integer> singlyLinkedList = new SinglyLinkedList<Integer>();
// creates 3 nodes
Node<Integer> first = new Node<Integer>(10);
Node<Integer> second = new Node<Integer>(20);
Node<Integer> third = new Node<Integer>(30);
// lets assign reference of first to head of singly linked list
singlyLinkedList.head = first;
// assign reference of second node to next of first
first.next = second;
// assign reference of third node to next of second
second.next = third;
// print the elements of the linked list
singlyLinkedList.printList();
}
}


No comments :
Post a Comment